
DNA analysis allows to:
- identify traces of biological tissue deposited on people or objects
- identify people, living or dead
The trace identification analysis is requested by a magistrate or a judicial police officer.
The objective is to find and identify the cells deposited by an aggressor or a victim.
This analysis has three parts:
Identification of cellular tissue
- Search for blood by chemical method
- Search for sperm by chemical and cytological methods
- Search for hair elements by physical method
- Search for epithelial cells, by taking samples in areas where the cells may have been deposited
Identification of the DNA in the tissues previously found or potentially present in the epithelial cells
After extraction, the DNA is amplified and genotyped for the autosomal DNA at 16 loci. The result is called a DNA profile.
Previously identified DNA profile is compared with the DNA profile from a sample taken from an identified person: victim – suspect – witness.
This trace profile matches or does not match the comparison profile.
Identification analysis of people, living or dead
The identification of a person can make in relation to his family, his ascendants or direct descendants.
These analyzes are performed:
- either for a paternity search
- or for a maternity search
- or to identify a corpse
Paternity or maternity searches
Above all, it is important to note that under French law, any paternity request must be presented before a judge of the Tribunal de Grande Instance, of the place of residence of the person in respect to whom the child seeks to establish their parentage.
This search consists of obtaining:
- A mouth swab of the child
- A mouth swab of the father
- A mouth swab of the mother
After extraction, the DNA from the mouth swabs is amplified and genotyped. Analysis of the DNA profiles of the father and the mother allows to detect whether there are any exclusions or not with the child’s profile.
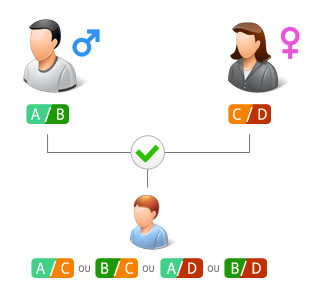
If the genotype of the child shows no exclusion from the parents, a likelihood calculation is performed to clarify the probability of paternity or maternity.
If the child’s profile has exclusions:
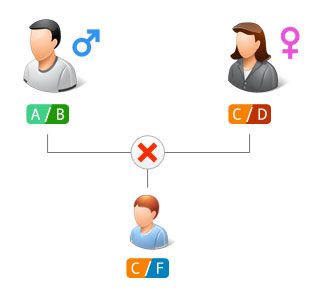
The alleged father is not the father of the child.
The identification of a corpse
This identification is based on the verification of a family relationship between the body to identify and close family: Parent / child.
The procedure used is identical to that described above. However, additional analyses are needed if the comparison is with less close family: brother, sister, uncle, aunt.
- Y chromosome analysis
- Mitochondrial DNA analysis
- X chromosome analysis


